Misdemeanor vs Felony: When it comes to criminal offenses, the terms “misdemeanor” and “felony” are often thrown around, but what do they really mean? While both refer to crimes, the severity, consequences, and legal implications of each are vastly different. Whether you’re trying to understand the legal system or facing charges yourself, knowing the difference between a misdemeanor and a felony is crucial. In this article, we’ll break down everything you need to know about these two categories of crimes, including examples, penalties, and how they differ across states like California.
What Is a Misdemeanor?
A misdemeanor is a less serious criminal offense compared to a felony. These crimes are typically punishable by fines, probation, community service, or short-term jail sentences (usually less than a year). Misdemeanors are often non-violent offenses, but there are exceptions.
Examples of Misdemeanors
Common examples of misdemeanors include:
- Petty theft (shoplifting or stealing items of low value)
- Simple assault (minor physical altercations without serious injury)
- Trespassing
- Disorderly conduct
- Driving under the influence (DUI) in some cases
For instance, if someone gets into a heated argument and pushes another person without causing injury, this could be classified as a misdemeanor assault. Similarly, stealing a small amount of money or property might result in a petty theft charge.
Penalties for Misdemeanors
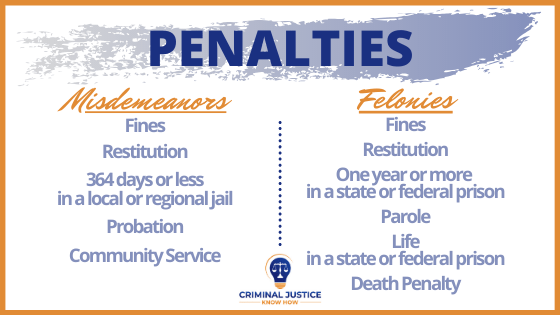
The penalties for misdemeanors vary by state but generally include:
- Fines ranging from a few hundred to a few thousand dollars
- Jail time of up to 364 days (often served in a local jail rather than a state prison)
- Probation or community service
In some cases, misdemeanors can be expunged from a person’s record after a certain period, depending on the state’s laws.
What Is a Felony?
Felonies are more serious crimes that carry harsher penalties. These offenses often involve violence, significant financial harm, or other severe consequences. Felonies can result in long-term imprisonment, hefty fines, and the loss of certain civil rights, such as the right to vote or own a firearm.
Examples of Felonies
Examples of felonies include:
- Murder or manslaughter
- Rape or sexual assault
- Kidnapping
- Arson
- Grand theft (stealing high-value items)
- Drug trafficking
For example, if someone commits a burglary and steals property worth thousands of dollars, they could face felony charges. Similarly, causing serious bodily harm to another person during an altercation could elevate an assault charge to a felony.
Penalties for Felonies
Felony penalties are significantly more severe than those for misdemeanors. They may include:
- Prison sentences of one year or more, potentially up to life imprisonment or even the death penalty in some states
- Fines ranging from thousands to hundreds of thousands of dollars
- Loss of civil rights, such as voting or firearm ownership
- Difficulty finding employment or housing due to a permanent criminal record
Misdemeanor vs Felony: Key Differences
While both misdemeanors and felonies are criminal offenses, the key differences lie in their severity, penalties, and long-term consequences.
Severity of the Crime
Misdemeanors are considered less severe and often involve minor offenses, while felonies are serious crimes that can have life-altering consequences for both the victim and the offender.
Penalties
- Misdemeanors: Typically result in shorter jail sentences (less than a year), smaller fines, and alternative punishments like probation or community service.
- Felonies: Can lead to long-term imprisonment, substantial fines, and the loss of civil rights.
Long-Term Consequences
A misdemeanor conviction may not drastically impact a person’s life, especially if the offense is expunged. However, a felony conviction can result in a permanent criminal record, making it difficult to secure employment, housing, or even loans.
Misdemeanor vs Felony vs Infraction
In addition to misdemeanors and felonies, there’s a third category of offenses: infractions. Infractions are minor violations, often punishable by fines but not jail time. Examples include traffic tickets, littering, or jaywalking.
Key Differences
- Infractions: No jail time, only fines.
- Misdemeanors: Up to a year in jail, fines, and other penalties.
- Felonies: One year or more in prison, hefty fines, and long-term consequences.
Misdemeanor vs Felony in California
California, like other states, has its own way of classifying crimes. Understanding how misdemeanors and felonies are defined in California can help clarify the legal process.
California Misdemeanors
In California, misdemeanors are punishable by up to one year in county jail and fines of up to $1,000. Examples include:
- Petty theft
- Simple assault
- First-time DUI
California Felonies
Felonies in California carry more severe penalties, including state prison sentences and higher fines. Examples include:
- Murder
- Robbery
- Drug trafficking
California also has a unique category called “wobbler” offenses, which can be charged as either a misdemeanor or a felony depending on the circumstances of the crime and the defendant’s criminal history.
How Misdemeanors Can Become Felonies
In some cases, repeated misdemeanor offenses can escalate to felony charges. For example:
- A first-time DUI is often a misdemeanor, but a third DUI within ten years can be charged as a felony.
- Petty theft is typically a misdemeanor, but repeated offenses can lead to felony charges.
This escalation is designed to deter repeat offenders and address patterns of criminal behavior.
FAQs About Misdemeanors and Felonies
1. What’s the difference between a misdemeanor and a felony?
A misdemeanor is a less serious crime with lighter penalties, while a felony is a more serious offense with harsher consequences, including longer prison sentences.
2. Can a misdemeanor be upgraded to a felony?
Yes, repeated misdemeanor offenses or certain aggravating factors can lead to felony charges.
3. What are some examples of misdemeanors?
Examples include petty theft, simple assault, and first-time DUI.
4. What are some examples of felonies?
Examples include murder, rape, and grand theft.
5. How do misdemeanors and felonies differ in California?
In California, misdemeanors are punishable by up to one year in county jail, while felonies can result in state prison sentences.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between misdemeanors and felonies is essential for navigating the legal system. While misdemeanors are less severe, they can still have significant consequences. Felonies, on the other hand, carry life-altering penalties and long-term repercussions. Whether you’re dealing with a misdemeanor or felony charge, it’s important to seek legal advice to understand your rights and options.
By knowing the distinctions between these two categories of crimes, you can better understand how the legal system works and what to expect if you or someone you know is facing charges.
Table: Misdemeanor vs Felony Comparison
| Aspect | Misdemeanor | Felony |
|---|---|---|
| Severity | Less serious | More serious |
| Jail Time | Up to 1 year (local jail) | 1 year or more (state prison) |
| Fines | Smaller fines | Larger fines |
| Long-Term Impact | Minimal | Significant |
By understanding these differences, you can better navigate the complexities of the legal system and make informed decisions.



