Cannabis is a complex plant with over 100 cannabinoids, each offering unique properties and effects. Among these, THCA (tetrahydrocannabinolic acid) and THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) are two of the most discussed compounds. While they share a close relationship, their effects, uses, and legal statuses differ significantly. This article dives deep into the world of THCA vs THC, exploring their chemical structures, effects, benefits, risks, and more. Whether you’re a cannabis enthusiast or someone seeking clarity, this guide will help you understand what sets these two compounds apart.
What is THCA?
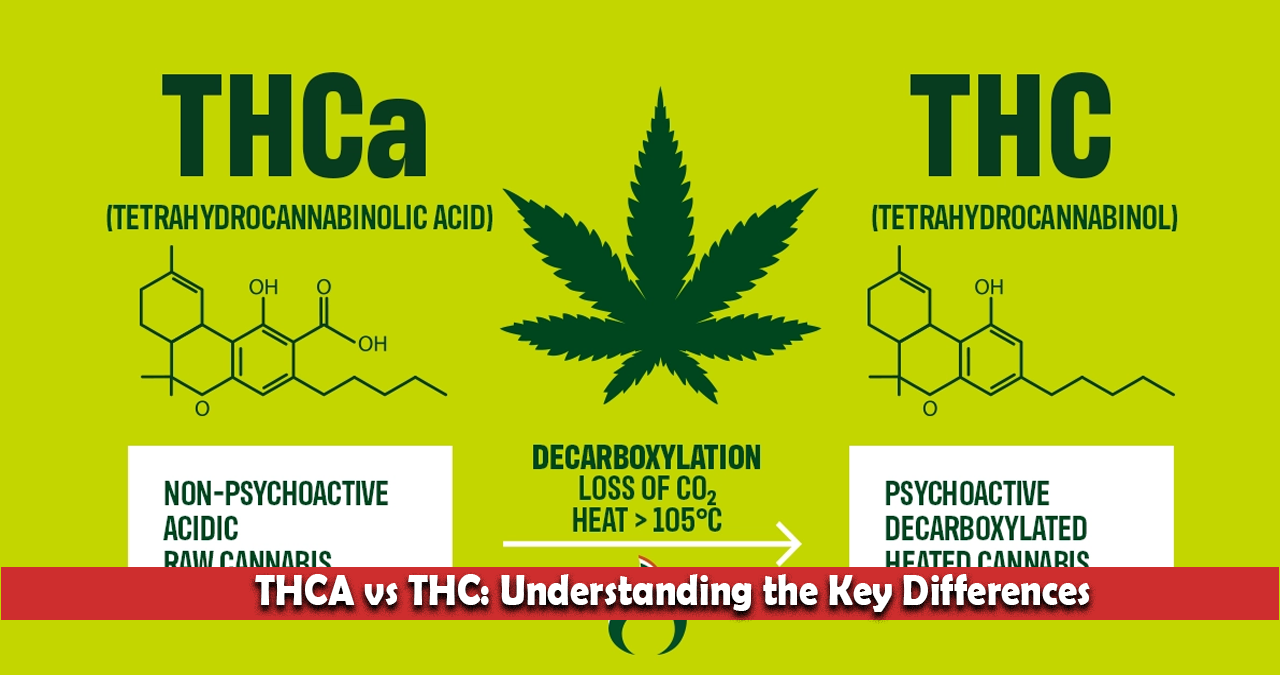
THCA, or tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid found in raw and unheated cannabis plants. It is the acidic precursor to THC and is abundant in fresh cannabis leaves and flowers. Unlike THC, THCA does not produce a “high” because it does not bind effectively to the brain’s cannabinoid receptors.
Key Characteristics of THCA
- Non-Psychoactive: THCA does not cause intoxication or mind-altering effects.
- Found in Raw Cannabis: It is present in fresh cannabis leaves, flowers, and stems.
- Potential Therapeutic Benefits: Early research suggests THCA may have anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective, and anti-nausea properties.
THCA is often consumed by juicing raw cannabis or using tinctures and topicals that preserve its acidic form. However, when exposed to heat (through smoking, vaping, or cooking), THCA undergoes decarboxylation, converting into THC and becoming psychoactive.
What is THC?
THC, or tetrahydrocannabinol, is the primary psychoactive compound in cannabis. It is responsible for the euphoric “high” that users experience. THC forms when THCA is heated, a process known as decarboxylation.
Key Characteristics of THC
- Psychoactive: THC binds to CB1 receptors in the brain, altering mood, perception, and cognition.
- Therapeutic Uses: THC is widely used for pain relief, appetite stimulation, and nausea control.
- Potential Risks: High doses of THC can cause anxiety, paranoia, and impaired memory or coordination.
THC is the most well-known cannabinoid and is often the focus of both recreational and medical cannabis use. However, its psychoactive nature makes it a subject of legal and health-related scrutiny.
THCA vs THC: Which is Stronger?

When comparing THCA vs THC, the question of strength often arises. The answer depends on the context:
- Psychoactive Strength: THC is stronger in terms of psyc effects. It directly interacts with the brain’s receptors, producing a high, while THCA does not.
- Therapeutic Potential: THCA may offer unique health benefits without the intoxicating effects of THC. However, more research is needed to fully understand its potential.
In essence, THCA is the “raw” form of THC, and its strength lies in its non-psychoactive properties. THC, on the other hand, is the “activated” form, known for its potent psychoactive effects.
Chemical Structure and Properties of THCA vs THC
The primary difference between THCA and THC lies in their chemical structures.
THCA’s Chemical Structure
THCA contains a carboxylic acid group, which makes it larger and more chemically stable in its raw form. This extra group prevents THCA from binding effectively to CB1 receptors in the brain, rendering it non-psychoactive.
THC’s Chemical Structure
When THCA is exposed to heat or light, it loses its carboxylic acid group through decarboxylation. This structural change allows THC to bind to CB1 receptors, producing psychoactive effects.
Impact on Effects
- THCA: Non-psychoactive, with potential therapeutic benefits.
- THC: Psychoactive, with both recreational and medical applications.
This small but significant difference in molecular structure determines how each compound interacts with the body and brain.
THCA vs THC Effects
THCA Effects
- Non-Psychoactive: No high or intoxication.
- Anti-Inflammatory: May help reduce inflammation and pain.
- Neuroprotective: Potential to protect brain cells from damage.
- Anti-Nausea: Could alleviate nausea and vomiting.
- Anti-Proliferative: Early studies suggest it may inhibit cancer cell growth.
THCA is ideal for individuals seeking the potential health benefits of cannabis without the psychoactive effects.
THC Effects
- Psychoactive: Produces euphoria, relaxation, and altered perception.
- Pain Relief: Effective for chronic pain management.
- Appetite Stimulation: Known for causing “the munchies.”
- Anti-Nausea: Helps cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy.
- Mood Changes: Can induce anxiety or paranoia in high doses.
THC is favored by recreational users and medical patients seeking relief from pain, nausea, or insomnia.
THCA vs THC Side Effects and Risks
THCA Side Effects
- Minimal Psychoactive Risk: Unlikely to cause anxiety or paranoia.
- Limited Research: More studies are needed to confirm its safety and efficacy.
- Potential Drug Interactions: May interact with certain medications.
THC Side Effects
- Psychoactive Effects: Can cause anxiety, paranoia, or impaired cognition.
- Dependency: Frequent use may lead to tolerance and withdrawal symptoms.
- Physical Effects: Dry mouth, red eyes, and increased heart rate.
While THCA is generally considered safer, THC’s psychoactive nature makes it more prone to misuse and dependency.
Legal Status of THCA vs THC
THC Legality
- Federal Law: THC is classified as a Schedule I substance in the U.S., making it illegal at the federal level.
- State Laws: Many states have legalized THC for medical or recreational use.
THCA Legality
- Non-Psychoactive: THCA is not explicitly listed as a controlled substance.
- Gray Area: Because THCA can convert into THC, its legal status is often ambiguous.
Always check local laws before purchasing or using THCA or THC products.
Consumption Methods for THCA and THC
Inhalation
- THC: Smoking or vaping cannabis delivers immediate psychoactive effects.
- THCA: Inhaling raw cannabis will not produce a high unless heated.
Edibles
- THC: Edibles provide a longer-lasting and often stronger high.
- THCA: Raw cannabis edibles retain THCA’s non-psychoactive properties.
Topicals and Tinctures
- THCA: Topicals and tinctures can deliver THCA’s potential benefits without psychoactivity.
- THC: These methods can also be used for localized pain relief.
How Long Do THCA and THC Stay in Your System?
THCA
- Half-Life: Not well-studied.
- Drug Tests: THCA is not typically detected in standard drug screenings.
THC
- Urine Tests: Detectable for 3–30 days, depending on usage frequency.
- Blood Tests: Detectable for 1–7 days.
- Hair Tests: Can show THC use for up to 90 days.
Is THCA or THC Addictive?
THCA
- Non-Addictive: No evidence suggests THCA is habit-forming.
THC
- Potentially Addictive: Regular use can lead to dependency and withdrawal symptoms.
Can You Overdose on THCA or THC?
Fatal overdoses from THCA or THC are virtually impossible. However, consuming too much THC can cause discomfort, such as anxiety, paranoia, or nausea. THCA, being non-psychoactive, does not pose this risk.
FAQs
1. What is THCA vs THC?
THCA is the non-psychoactive precursor to THC. When heated, THCA converts into THC, which is psychoactive.
2. THCA vs THC: Which is stronger?
THC is stronger in terms of psychoactive effects, while THCA offers potential therapeutic benefits without intoxication.
3. Can THCA get you high?
No, THCA is non-psychoactive and does not produce a high.
4. Is THCA legal?
THCA is not explicitly regulated, but its legal status can be ambiguous due to its potential to convert into THC.
5. How does THCA turn into THC?
THCA converts into THC through decarboxylation, which occurs when cannabis is heated.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between THCA and THC is essential for making informed decisions about cannabis use. While THCA offers potential health benefits without psychoactivity, THC is known for its recreational and medical effects. Both compounds have unique properties, and their effects, risks, and legal statuses vary widely. Whether you’re exploring cannabis for wellness or recreation, knowing the distinction between THCA and THC can help you choose the right product for your needs.
External Links:
This comprehensive guide ensures you have all the information you need to navigate the world of THCA and THC confidently.